Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
- Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that damages blood vessels in the retina. If left untreated, it can impair vision and may lead to blindness.
- Early stages often show no clear symptoms. As the condition progresses, patients may notice floaters, blurred vision, or flashes of light. Severe cases can cause partial or total vision loss.
- Treatment depends on the disease stage and may include blood sugar control, medication, laser therapy, intravitreal injections, or retinal surgery to prevent permanent vision damage.
Vision is essential for daily life. However, for people with diabetes, eyesight can be threatened by a condition known as diabetic retinopathy. If early warning signs are overlooked or proper care is delayed, permanent vision loss may occur. This article explains the causes of diabetic retinopathy, warning symptoms that should not be ignored, and ways to protect your eyesight safely and effectively.
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is an eye complication caused by diabetes. Persistently high blood sugar damages small blood vessels in the retina, leading to leakage, bleeding, or abnormal new vessel growth. These changes can result in blurred vision and, if untreated, blindness.
In early stages, symptoms may not be noticeable. As the disease becomes more severe, vision can deteriorate significantly. Therefore, people with diabetes should undergo comprehensive eye examinations at least once a year for early detection and timely treatment.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy develops gradually due to progressive retinal blood vessel damage and can be divided into two main stages:
Early Stage (Non-Proliferative DR)
Retinal blood vessels weaken and form microaneurysms, leading to small hemorrhages, lipid leakage, nerve fiber ischemia, and possible retinal swelling. Without treatment, this stage may progress to a more severe form.
Advanced Stage (Proliferative DR)
Abnormal new blood vessels form and are fragile, causing bleeding into the vitreous. Scar tissue may pull on the retina, leading to retinal tears or detachment and severe vision loss or blindness. Immediate and close treatment is required.
If new vessels grow on the iris, fluid drainage can be blocked, increasing eye pressure and causing neovascular glaucoma, a difficult-to-treat condition that can also result in blindness.
Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is closely related to blood sugar levels and vascular health. Risk factors include:
- Chronic high blood sugar – weakens and damages retinal blood vessels
- High blood pressure – accelerates vascular damage and bleeding risk
- High cholesterol and abnormal blood lipids – causes vessel blockage and retinal deposits
- Long duration of diabetes – risk increases after 5–10 years
- Smoking – constricts blood vessels and worsens disease progression
- Pregnancy or gestational diabetes – hormonal changes increase risk
- Older age and genetics – natural vascular degeneration and family history raise susceptibility
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Common and Early Symptoms
- Blurred or fluctuating vision
- Floating black spots or web-like lines (floaters)
- Distorted images
- Reduced visual clarity
- Difficulty distinguishing colors
Severe Symptoms and Complications
- Dark or shadowed areas in vision
- Sudden increase in floaters due to vitreous bleeding
- Flashes of light from retinal traction
- Partial or sudden vision loss
These symptoms may indicate serious conditions such as vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment. Early treatment greatly reduces the risk of permanent vision loss.
Diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy
Eye examinations assess retinal and vascular health to detect abnormalities early:
- Basic vision testing – visual acuity and screening
- Dilated eye examination – detailed retinal assessment
- Fundus photography – documents retinal changes
- Fluorescein angiography – identifies leakage and abnormal vessels
- OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) – measures retinal thickness and swelling
- Additional tests in severe cases, such as intraocular pressure measurement
People with diabetes should have a retinal exam at least once a year.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy
1. Medication
Used in early stages or mild retinal swelling:
Eye drops or oral medication to reduce inflammation
Injectable medications to reduce vascular leakage
Always combined with blood sugar, blood pressure, and lipid control.
2. Laser Treatment
Recommended for retinal swelling or advanced disease:
Focal laser seals leaking vessels
Panretinal photocoagulation reduces abnormal vessel growth
Laser treatment slows vision loss but may slightly affect peripheral or night vision.
3. Intravitreal Injections
Anti-VEGF or steroid injections reduce swelling and abnormal vessel growth. Repeated injections may be required under ophthalmologist supervision.
4. Vitrectomy Surgery
Used in severe cases with vitreous bleeding or retinal detachment. Surgery removes blood-filled vitreous and repairs retinal damage. Close postoperative follow-up is essential.
How to Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy
Maintain good blood sugar control
Control blood pressure and cholesterol
Have regular eye examinations
Quit smoking and limit alcohol
Exercise regularly
Eat a balanced diet
Protect eye health and avoid eye injuries
Self-Care for Diabetic Patients to Prevent Blindness
Attend regular eye checkups
Maintain HbA1C below 7%
Control blood pressure and lipid levels
Quit smoking
Exercise regularly
Take medications as prescribed
Consult doctors to fully understand the condition
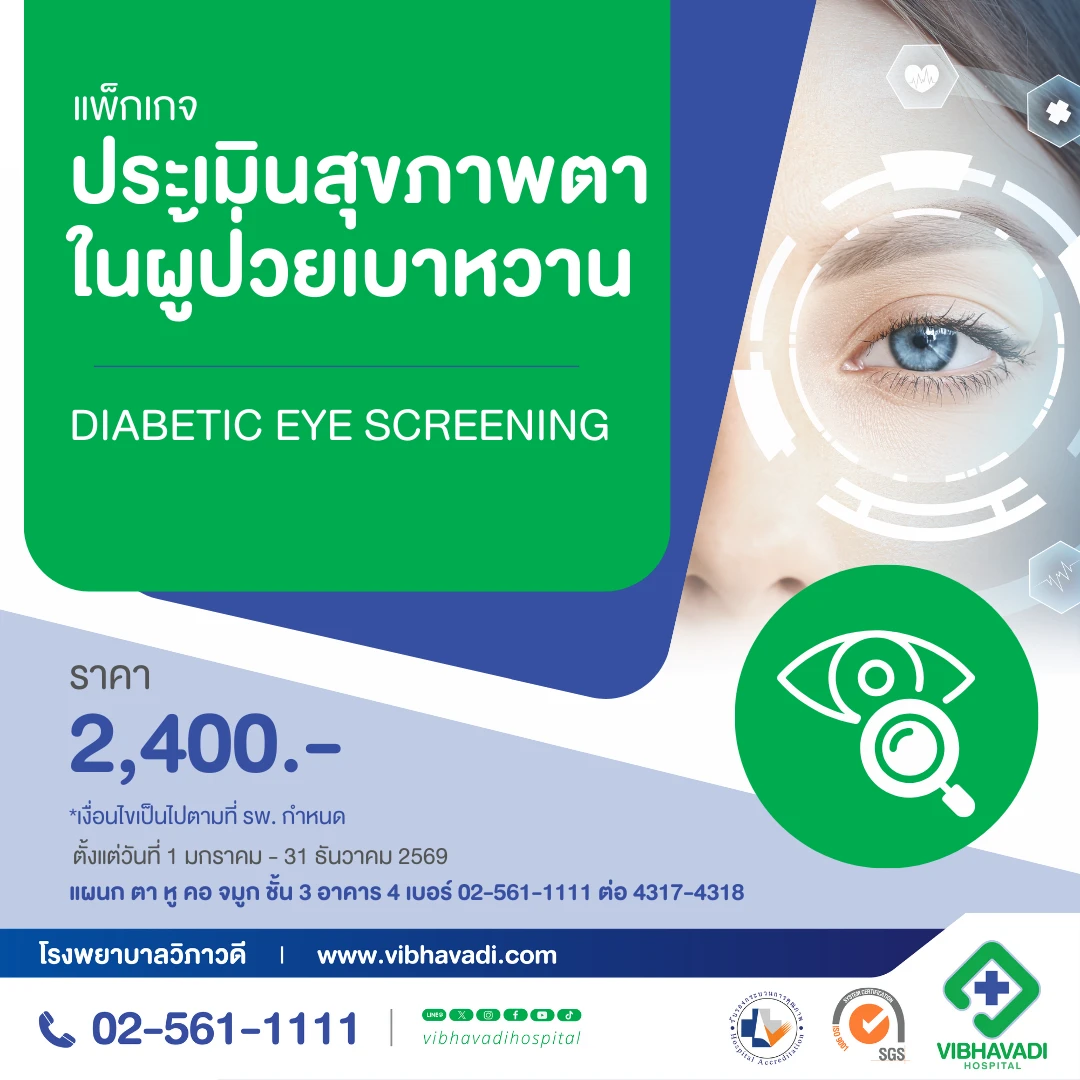
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening & Treatment at Vibhavadi Hospital
Vibhavadi Hospital provides comprehensive diabetic retinopathy screening and treatment using advanced diagnostic tools and expert ophthalmologists. Personalized treatment plans are tailored to disease severity, focusing on early detection, prevention of progression, and preservation of vision.
Summary
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that damages retinal blood vessels and may lead to blindness if untreated. Early stages may show no symptoms, but regular eye exams allow early detection and effective treatment. With proper care, blood sugar control, and timely medical intervention, long-term vision can be preserved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is diabetic retinopathy dangerous?
Yes. If untreated, it can gradually damage the retina and lead to permanent vision loss. Regular screening is essential.
How long does it take for diabetic retinopathy to cause blindness?
It varies by individual and depends on blood sugar control and overall health. Poorly controlled diabetes over many years increases the risk.
Can diabetic retinopathy be cured?
It cannot be completely cured, but disease progression can be controlled and vision preserved with proper treatment.
Are eye check-up packages available?
Vibhavadi Hospital offers comprehensive eye health programs, including retinal screening with fundus photography for early diagnosis and care.