Lymphoma
Overview
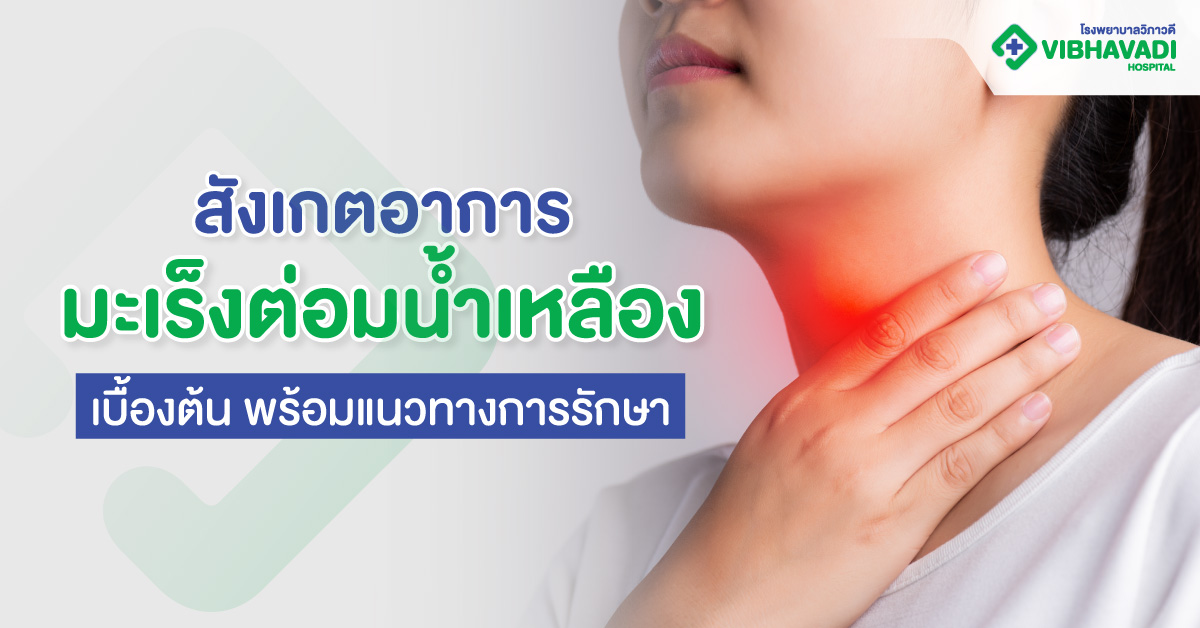
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system — a vital part of the immune system. It involves the abnormal growth of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that helps the body fight infections. Lymphoma can affect lymph nodes, the spleen, bone marrow, and other organs throughout the body.
There are two main types of lymphoma: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Each type has its own subtypes, treatment strategies, and prognoses. Early detection and appropriate medical care are crucial for improving patient outcomes.
Symptoms of Lymphoma
Lymphoma can present with a wide range of symptoms, often similar to other illnesses. Common symptoms include:
- Painless swelling of lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin
- Unexplained fever
- Night sweats
- Persistent fatigue
- Sudden weight loss
- Itching
- Shortness of breath or chest pain
- Recurrent infections
These symptoms may appear gradually or suddenly and can sometimes be mistaken for viral infections.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of lymphoma remains unknown, but certain factors may increase the risk:
- Weakened immune system (e.g., HIV/AIDS, autoimmune diseases)
- Certain infections (e.g., Epstein-Barr virus, Helicobacter pylori, hepatitis C)
- Exposure to chemicals such as pesticides
- Family history of lymphoma
- Age (some types are more common in younger adults, while others occur in older age groups)
- Previous radiation or chemotherapy
While risk factors exist, many people with lymphoma have no known predisposing condition.
Types of Lymphoma
Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL)
- Characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells under the microscope
- Typically affects younger people
- Highly treatable, especially in early stages
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)
- More common than HL
- Comprises many subtypes (e.g., diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma)
- Some forms grow rapidly (aggressive), while others are slow-growing (indolent)
Diagnosis at Vibhavadi Hospital
Early and accurate diagnosis is critical in managing lymphoma. At Vibhavadi Hospital, we utilize state-of-the-art technology for thorough evaluation:
- Physical examination and medical history
- Blood tests: Complete blood count, LDH levels, liver/kidney function tests
- Imaging tests: CT scan, PET scan, or MRI to determine cancer spread
- Lymph node biopsy: Removal of tissue sample for histopathology
- Bone marrow biopsy: To detect if lymphoma has spread to the bone marrow
Our team ensures rapid diagnostic processing with multidisciplinary collaboration to form the most accurate treatment plan.
Staging of Lymphoma
Lymphoma is categorized into four stages:
- Stage I: Involvement of a single lymph node region or organ
- Stage II: Two or more lymph node regions on the same side of the diaphragm
- Stage III: Lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm are affected
- Stage IV: Widespread involvement of one or more organs outside the lymphatic system
Staging helps determine the extent of the disease and guide treatment options.
Treatment Options at Vibhavadi Hospital
Treatment for lymphoma depends on the type, stage, patient’s health, and whether the disease is aggressive or indolent. Vibhavadi Hospital offers comprehensive and personalized treatment strategies.
Chemotherapy
- Primary treatment for both HL and NHL
- Combination drug regimens tailored to lymphoma subtype (e.g., ABVD, CHOP)
- Administered in cycles with close monitoring of side effects
Radiation Therapy
- Often used in early-stage HL or localized NHL
- Precisely targets lymph nodes to reduce tumor mass
- Can be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy
Targeted Therapy
- Drugs like rituximab target specific proteins on lymphoma cells (e.g., CD20)
- Effective in B-cell lymphomas
- Less damage to normal cells compared to traditional chemotherapy
Immunotherapy
- Utilizes the body’s immune system to fight cancer
- CAR T-cell therapy and checkpoint inhibitors are options in some advanced cases
Stem Cell Transplant
- For patients who relapse or have aggressive disease
- High-dose chemotherapy followed by infusion of healthy stem cells
- Autologous or allogeneic transplant depending on the case
Supportive Care
- Symptom relief and management of side effects
- Nutritional support and psychological counseling
- Ongoing monitoring and survivorship planning
Why Choose Vibhavadi Hospital for Lymphoma Treatment
- Multidisciplinary care from hematologists, oncologists, pathologists, radiologists, and nursing teams
- Cutting-edge diagnostic and imaging facilities
- Personalized treatment plans according to global guidelines
- Emphasis on patient quality of life and holistic care
- Accessible inpatient and outpatient oncology services
Follow-Up and Long-Term Monitoring
After completing treatment, patients require routine monitoring to detect recurrence, manage side effects, and maintain overall health. This may include:
- Regular physical exams
- Periodic imaging scans
- Blood tests
- Vaccinations and infection prevention for immunocompromised individuals
Our long-term care team ensures continuous support for lymphoma survivors.
Insurance Coverage and Costs
Vibhavadi Hospital accepts most major public and private health insurance plans. Services that may be covered include:
-
Diagnostic evaluations and lab work
-
Inpatient and outpatient chemotherapy
-
Radiation therapy and medications
-
Follow-up appointments and supportive care
Our financial counselors are available to assist patients in understanding their insurance benefits and estimating treatment costs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is lymphoma curable?
Yes. Many types of lymphoma, especially Hodgkin lymphoma and some non-Hodgkin lymphomas, are highly treatable and curable with timely treatment.
Q2: What’s the difference between Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Hodgkin lymphoma is defined by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, whereas non-Hodgkin lymphoma includes a diverse group of lymphatic cancers without these cells.
Q3: Can lymphoma come back after treatment?
Yes, recurrence is possible. Patients are monitored regularly after treatment to detect relapse early and manage it effectively.
Q4: Is lymphoma contagious?
No. Lymphoma is not infectious and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
Q5: How can I lower my risk of developing lymphoma?
While not all cases are preventable, maintaining a healthy immune system, avoiding known risk factors (e.g., infections, chemicals), and seeking medical attention for unexplained symptoms can help.
Testimonials
Proud to take care of you