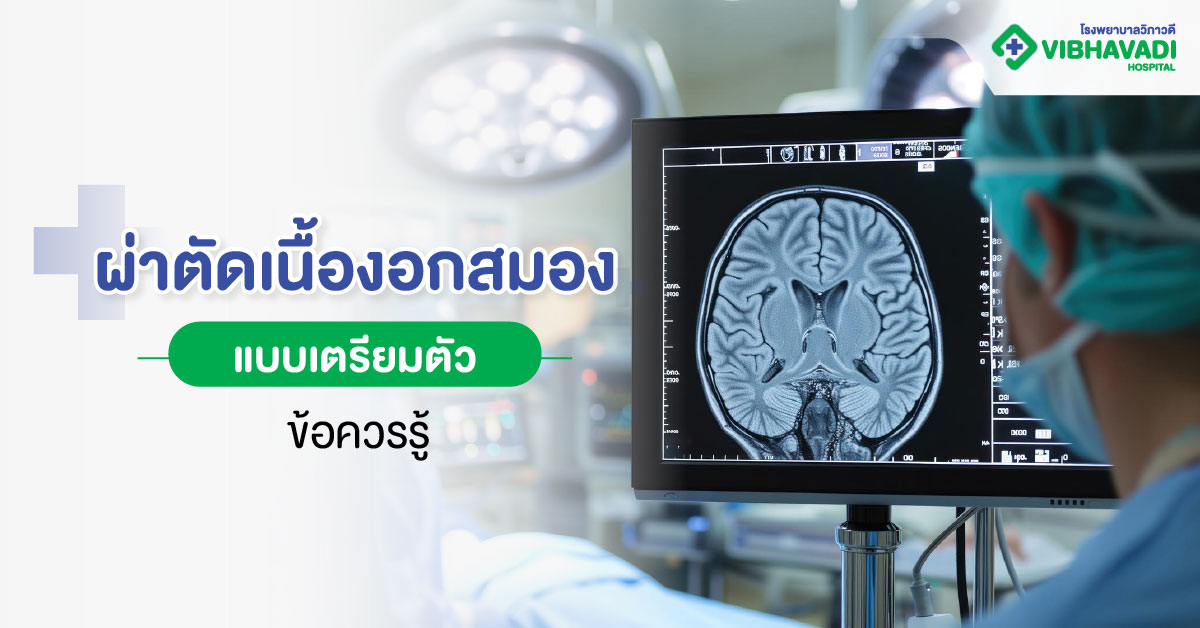
ฺBrain Tumor Surgery
Key Takeaway
Brain tumor surgery involves removing the tumor to relieve pressure and protect critical brain tissue. While there are risks, careful planning and treatment by experienced neurosurgeons can minimize complications and improve recovery outcomes.
Brain tumors occur when brain cells grow abnormally. Causes may include genetic mutations, exposure to carcinogens, or environmental factors. In some cases, the exact cause is unknown. Regular health check-ups and monitoring symptoms can help detect tumors early.
Brain tumor surgery can be performed using different approaches, such as open craniotomy (removing the tumor directly) or minimally invasive techniques like endoscopy or laser surgery, which result in smaller incisions and faster recovery. The choice of treatment depends on the tumor’s size, type, and location.
Is Brain Tumor Surgery Dangerous?
A brain tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue inside the brain, which may be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Surgery is performed to reduce tumor size or remove it entirely, helping to relieve symptoms and prevent further growth.
Although surgery improves survival and quality of life, risks include infection, bleeding, or damage to nearby brain tissue, which may cause problems with movement, speech, or memory. Risks depend on the tumor’s location, size, type, and the patient’s overall health. Consultation with a specialized neurosurgeon is essential for safe treatment planning.
Types of Brain Tumors
-
Benign Brain Tumors – Slow-growing, usually non-invasive, but can still compress nearby tissue. Examples: meningioma, pituitary adenoma.
-
Malignant Brain Tumors – Fast-growing, invasive, and prone to recurrence. Example: glioblastoma multiforme.
-
Primary Brain Tumors – Originate from brain cells (e.g., glial cells, meninges).
-
Secondary (Metastatic) Brain Tumors – Spread from cancers in other organs, such as the lungs, breast, or liver.
Causes and Risk Factors
Brain tumors develop due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors:
-
Genetic Factors – Some cases are linked to inherited syndromes (e.g., Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Neurofibromatosis) that increase susceptibility to abnormal cell growth.
-
Environmental Factors – Exposure to radiation, toxic chemicals, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or other long-term lifestyle risks can damage brain cells and trigger tumor formation.
Warning Signs of a Brain Tumor
Symptoms vary depending on the tumor’s location and size, but common signs include:
-
Persistent headaches not relieved by medication
-
Seizures or loss of body control
-
Vision problems (blurred vision, double vision, blind spots)
-
Balance or coordination issues, weakness, or numbness
-
Speech or language difficulties
-
Personality or behavioral changes (e.g., depression, irritability, anxiety)
-
Unexplained nausea and vomiting
Diagnostic Methods
Accurate diagnosis requires multiple tests to determine the tumor’s type, size, and position:
-
CT Scan – X-ray imaging to identify brain structure and masses.
-
MRI – High-resolution imaging, often enhanced with contrast agents, ideal for soft tissue.
-
EEG – Detects abnormal brain activity related to seizures.
-
Biopsy – Extracting a tissue sample for microscopic analysis.
-
Lumbar Puncture – Analyzing cerebrospinal fluid to detect abnormal cells.
Types of Brain Tumor Surgery
-
Craniotomy (Open Surgery) – Removing part of the skull to excise the tumor. Best for large or complex tumors. Offers maximal removal but carries risks of infection, bleeding, and longer recovery.
-
Neuroendoscopy (Endoscopic Surgery) – Uses a small camera inserted through a natural opening or a tiny incision. Minimally invasive, with smaller wounds, less pain, and quicker recovery.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Not all brain tumors require immediate surgery. Alternatives include:
-
Radiation Therapy – Destroys tumor cells with targeted radiation.
-
Chemotherapy – Uses drugs to kill or shrink tumors.
-
Targeted Therapy – Focuses on specific cancer cell mechanisms.
-
Watchful Waiting – Monitoring slow-growing tumors with regular scans.
-
Palliative Care – Relieves symptoms and maintains quality of life.
Pre- and Post-Surgery Care
Before Surgery:
-
Complete health evaluation and medical consultation
-
Inform doctors of allergies and medications
-
Fasting as instructed
-
Mental preparation and understanding risks
-
Arranging post-surgery care and assistance
After Surgery:
-
Adequate rest, avoiding strenuous activity
-
Take prescribed medications as directed
-
Monitor for warning signs (severe headache, seizures, weakness, vomiting)
-
Attend follow-up appointments
-
Adopt healthy habits (stress management, balanced diet, avoiding head injury)
Recovery and Risks
-
Surgery Duration – Usually 3–8 hours, depending on complexity
-
Hospital Stay – Typically 3–10 days, with further rehabilitation lasting weeks to months
-
Possible Side Effects:
-
Headache, swelling around incision
-
Infection or bleeding
-
Neurological problems (speech, vision, movement difficulties)
-
Recurrence depending on tumor type
-
Brain Tumor Surgery at Vibhavadi Hospital
At the Neurology Center, Vibhavadi Hospital, surgery is performed by specialized neurosurgeons using advanced technologies such as CT Scan, MRI, and Neuro-navigation to improve precision and safety. Comprehensive post-operative care includes rehabilitation, follow-up monitoring, and management of side effects, ensuring safe treatment and better recovery outcomes.
Conclusion
Brain tumor surgery is a crucial treatment for patients whose tumors affect brain function. Symptoms include persistent headaches, seizures, speech or vision problems, and nausea. Diagnosis involves CT, MRI, EEG, biopsy, or lumbar puncture. Treatment may include open surgery, endoscopic surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or targeted therapies depending on the tumor.
Risk factors include genetics, environmental exposures, and lifestyle habits. Careful preparation before and after surgery helps improve recovery. Regular health check-ups remain the best prevention, allowing early detection and timely treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the chances of a full recovery?
It depends on the tumor’s type, size, and location, as well as the patient’s health. Some benign tumors can be completely removed, while malignant ones may require ongoing treatment.
2. Are there alternatives to surgery?
Yes. Options include Gamma Knife radiosurgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the tumor’s nature and severity.
3. Can I return to normal life after surgery?
Most patients recover and resume daily activities. Rehabilitation and following medical advice are key to recovery.
4. How much does brain tumor surgery cost?
Costs vary depending on the surgical method, hospital stay, and technologies used. Please contact Vibhavadi Hospital directly for an accurate estimate.
Testimonials
Proud to take care of you