Laparoscopic hysteroscopy: Small incision, less pain, faster
- Hysteroscopy is a procedure that uses a small camera to view the uterus for diagnosis or treatment of abnormalities. It is suitable for women with irregular menstruation, infertility, recurrent miscarriages, or suspected uterine abnormalities.
- The advantages of hysteroscopy include a clear view of the uterine cavity, less pain, smaller incisions, faster recovery, the ability to examine and treat in a single procedure, and reduced risks associated with open abdominal surgery and infection.
- Most hysteroscopy incisions heal quickly, allowing women to return to their normal activities within 1-2 days and even go home the same day. However, for complex abnormalities, a 2-3 day recovery period may be required.
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses a small camera inserted through the vagina to visualize the inside of the uterus. It allows for accurate diagnosis and treatment of abnormalities, minimizes tissue damage, causes less pain, and results in a shorter recovery time. It avoids the need for an abdominal incision and is suitable for women with irregular menstruation, infertility, or suspected uterine polyps or adhesions. Treatment is performed by experienced obstetricians and gynecologists for optimal and effective results.
/Vibhavadi%20Hospital%20-%20Nov%2012%20(%E0%B8%9C%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%B2%E0%B8%95%E0%B8%B1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%AA%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%81%E0%B8%A5%E0%B9%89%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%A1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%A5%E0%B8%B9%E0%B8%81)%20(2).jpg)
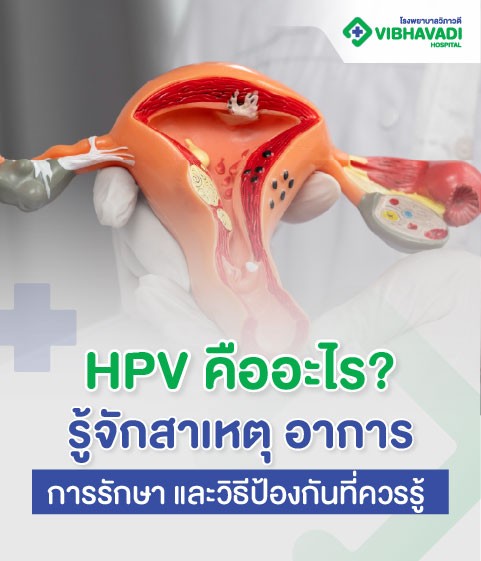
What is hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy is a gynecological procedure where a doctor inserts a small camera through the vagina and cervix into the uterus to directly view the inside of the uterus. It can be used for both diagnostic purposes, such as checking for the cause of abnormal bleeding, infertility, polyps, submental tumors, or adhesions in the uterus, and for therapeutic purposes, such as removing polyps, adhesions, small tumors, or enclosed contraceptive devices. The advantages include minimally invasive surgery, no abdominal incision, faster recovery, less pain, and more precise treatment.
/Vibhavadi%20Hospital%20-%20Nov%2012%20(%E0%B8%9C%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%B2%E0%B8%95%E0%B8%B1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%AA%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%81%E0%B8%A5%E0%B9%89%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%A1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%A5%E0%B8%B9%E0%B8%81)%20(3).jpg)
Who is Hysteroscopy Suitable for?
Hysteroscopy is suitable for women with gynecological abnormalities suspected to be caused by abnormalities within the uterus, or for those who want to investigate the cause of menstrual problems, infertility, and recurrent miscarriages, as well as those with abnormalities that can be treated hysteroscopy without open abdominal surgery. It allows for more accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
Indications for Hysteroscopy:
- Irregular menstruation, heavy or prolonged bleeding, or significant blood clots may indicate polyps or tumors under the uterine lining.
- Abnormal bleeding, especially after intercourse or menopause, may be related to endometrial abnormalities.
- Infertility: Used to assess the condition of the uterine lining before IUI or IVF.
- Recurrent miscarriage: To detect anatomical abnormalities that are not clearly visible on ultrasound.
- Suspected uterine abnormalities, such as adhesions, septum, or uterine malformations.
- Abnormal ultrasound results: Used to confirm and plan appropriate treatment.
Indications for Treatment:
- Endometrial polyps: Cause abnormal bleeding and reduce the chances of pregnancy. They can be removed hysterically.
- Submucous myomas are a cause of heavy periods and recurrent miscarriages. Removal can improve symptoms.
- Asherman syndrome (adhesions in the uterus) can cause light periods or infertility. Removing the adhesions can help restore the uterine lining.
- Uterine septum is a congenital abnormality that increases the risk of miscarriage. Removing the septum improves the chances of successful pregnancy.
- Removal of foreign objects, such as retained or displaced IUDs, which can cause inflammation or abnormal bleeding.
Who is not suitable for hysteroscopy?
- Women who are pregnant or suspect they are pregnant: Hysteroscopy may stimulate uterine contractions and increase the risk of miscarriage or harm to the fetus.
- Women with pelvic or vaginal infections: Hysteroscopy may spread the infection into the uterus and bloodstream.
- Women who experience excessive bleeding during the procedure: Large amounts of blood can obscure visibility and increase the risk of complications.
- Women with severe cervical stenosis: This makes insertion of the hysteroscope difficult and carries a risk of injury or perforation of the uterus.
- Patients with severe heart or lung conditions may not be suitable for general anesthesia or for procedures involving changes in body pressure.
- Patients allergic to saline or gases used to expand the uterus may experience severe allergic reactions or complications from these fluids or gases.
- Patients with bleeding disorders or abnormal blood clotting patterns have an increased risk of excessive bleeding and difficulty stopping bleeding after the procedure.
- Patients with advanced cervical cancer may experience the spread of cancer cells or increased bleeding during colposcopy.
- Patients with acute infections, such as high fever, should have the infection treated first to reduce the risk of complications.
- Patients who cannot lie supine for extended periods, such as those with spinal, lung, or circulatory problems, may have risks during examinations or surgery.
/Vibhavadi%20Hospital%20-%20Nov%2012%20(%E0%B8%9C%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%B2%E0%B8%95%E0%B8%B1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%AA%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%81%E0%B8%A5%E0%B9%89%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%A1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%A5%E0%B8%B9%E0%B8%81)%20(4).jpg)
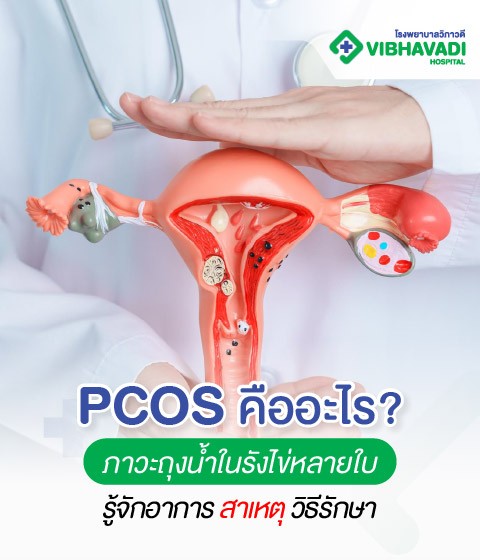
Reasons to Consider Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a procedure that allows doctors to directly visualize the inside of the uterus, enabling simultaneous diagnosis and treatment. It is suitable for women with gynecological abnormalities, fertility problems, or uterine abnormalities requiring precise correction.
1. Diagnosis of Uterine Abnormalities
Hysteroscopy allows doctors to clearly see the uterine lining, endometrium, and internal structures, enabling them to pinpoint the cause of abnormalities, such as:
- Irregular menstruation, heavy, prolonged, or more frequent bleeding than normal due to polyps or tumors.
- Spotting after menopause may indicate endometrial abnormalities.
- Unusually severe menstrual cramps may be caused by adhesions or masses obstructing menstrual flow.
2. Treatment of Infertility
In women with infertility, laparoscopy helps identify and correct abnormalities that interfere with embryo implantation and pregnancy, such as:
- Septate uterus, which reduces implantation space and increases the risk of miscarriage.
- Asherman’s syndrome, which causes incomplete endometrial lining and hinders implantation.
- Polyps or tumors that obstruct the uterus, interfering with embryo movement and implantation.
3. Surgical Removal of Abnormalities
Laparoscopy allows for the removal of abnormalities without major surgery, reducing scarring and recovery time. Examples include:
- Endometrial polyps, which can cause abnormal bleeding and infertility.
- Submucosal myomas, which can cause heavy, painful periods or recurrent miscarriages.
- Removal of foreign objects, such as retained or displaced IUDs, which can cause inflammation or abnormal bleeding.
/Vibhavadi%20Hospital%20-%20Nov%2012%20(%E0%B8%9C%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%B2%E0%B8%95%E0%B8%B1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%AA%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%81%E0%B8%A5%E0%B9%89%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%A1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%A5%E0%B8%B9%E0%B8%81)%20(5).jpg)
Advantages of Hysteroscopy:
- Clear view of the uterine cavity: The doctor can directly see inside the uterine cavity, allowing for a detailed assessment of the uterine lining and any abnormalities.
- More accurate diagnosis than ultrasound or D&C (dilation and curettage): Because it's a direct visual examination, not an assessment based on shadows or tissue sampling.
- Reduces the chance of missing diseases, especially small polyps, adhesions, or tiny lesions that may not be visible on ultrasound.
- Less pain and lower risk of complications: It's a small-incision procedure that doesn't disturb surrounding tissues much.
- No need for open abdominal surgery: Reduces the risk of large surgical scars, such as infection or adhesions after surgery.
- Small incision, faster recovery: Patients can return to their daily lives within a few days.
- Reduced risk of infection: Due to the small incision and short surgery time.
- Day Surgery: No need for multiple hospital stays, saving time and money.
- Can be examined and treated in one visit: If abnormalities are found, the doctor can treat them immediately without scheduling further surgery.
Preparation Before Hysteroscopy
Proper preparation helps ensure a smooth and accurate hysteroscopy procedure and reduces the risk of complications. Your doctor will provide specific instructions based on your individual physical condition. Generally, the ideal time for a hysteroscopy is about 3-7 days after the end of your menstrual period, as the uterine lining is clean, clearly visible, and you are not yet in the ovulation period.
- Inform your doctor about any drug allergies or pre-existing medical conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or blood disorders, so they can plan the appropriate and safe use of anesthesia and pain medication.
- Refrain from food and drink as instructed by your doctor. If general anesthesia or local anesthesia is used, your doctor will specify a fasting period to prevent vomiting or aspiration during the procedure.
- Avoid sexual intercourse for approximately 24-48 hours before the procedure to reduce the risk of infection and ensure a clean uterine lining.
- If you are pregnant or suspect you are pregnant, inform your doctor immediately. Hysteroscopy is not suitable for pregnant women as it may harm the baby.
- Arrange for someone to take you home if general anesthesia is required. Because patients may still experience drowsiness or slow responses after anesthesia, a companion is necessary for safety.
Hysteroscopy Procedure
Generally, a hysteroscopy procedure takes 15-45 minutes, depending on the complexity of the procedure. The main steps are as follows:
- Pre-operative preparation: The doctor will review your medical history, perform a physical examination, and provide instructions regarding fasting and other preparations.
- Administer local or general anesthesia as appropriate: Local anesthesia or short-acting anesthesia may be used depending on the complexity and the patient's comfort level.
- Insertion of a camera through the cervix into the uterus: A small camera allows the doctor to clearly see inside the uterus.
- Dilation of the uterine cavity with saline or gas: This widens the uterine cavity to provide a clearer view of the uterine wall and lining.
- Examination for abnormalities: The doctor assesses the condition of the uterine lining, adhesions, polyps, or tumors.
- If treatment is necessary, the doctor will use instruments through the camera to perform procedures such as removing polyps, dissecting adhesions, or removing small tumors without opening the abdomen.
- End of the procedure and a short recovery period: Most patients can go home the same day.
/Vibhavadi%20Hospital%20-%20Nov%2012%20(%E0%B8%9C%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%B2%E0%B8%95%E0%B8%B1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%AA%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%81%E0%B8%A5%E0%B9%89%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%A1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%A5%E0%B8%B9%E0%B8%81)%20(6).jpg)
Post-Surgery Care After Hysteroscopy
Most patients recover quickly after hysteroscopy, but proper self-care helps reduce the risk of infection and complications, allowing the body to return to normal more quickly.
- Get enough rest: You should rest and avoid strenuous activity in the first few days after surgery to allow your body to recover.
- Avoid strenuous exercise for 1-2 days to prevent injury or bleeding within the uterus.
- Avoid sexual intercourse for 1 week to prevent infection and allow the uterus to fully recover.
- If you experience a high fever, severe abdominal pain, or heavy bleeding, seek immediate medical attention. This includes high fever, severe abdominal pain, heavy bleeding, or an unusual odor.
Possible Symptoms After Hysteroscopy
Most patients recover quickly after hysteroscopy with mild symptoms. However, some may experience minor symptoms, which are normal and usually resolve on their own within 1-2 days.
- Slight lower abdominal pain: This is normal after uterine dilation and instrument placement. Rest is recommended, and you can use pain medication prescribed by your doctor.
- Spotting for 1-2 days: You may experience slight bleeding after the hysteroscopy. This is normal as the uterus recovers.
- You may feel slightly fatigued as your body is still recovering from the procedure and the anesthesia/sedation. Get enough rest and drink plenty of water.
Hysteroscopy: Risks and Potential Complications
Although hysteroscopy is a relatively safe and minimally invasive procedure, it still carries potential risks and complications. Your doctor will assess the risks and provide appropriate preventative care. Most complications are rare and treatable.
- Excessive bleeding may occur due to injury to the uterine lining or the removal of polyps/tumors. Seek immediate medical attention if bleeding is severe.
- Infection may occur in the uterine cavity or pelvic cavity, causing fever, abdominal pain, or an unusual odor. Monitor for symptoms and seek immediate medical attention.
- Uterine perforation or injury to nearby organs such as the intestines or bladder is rare but considered a serious complication.
- Temporary urinary or bladder dysfunction may occur due to irritation from the insertion of instruments.
- Lower abdominal pain or discomfort after the procedure is normal and usually resolves within 1-2 days.
- Persistent or prolonged spotting may occur; some individuals may experience minor bleeding for 3-5 days after the procedure.
Is Hysteroscopy Dangerous?
Hysteroscopy is a low-risk procedure when performed by a skilled surgeon. It involves minimal incisions, a short operating time, and quick recovery for most patients. Severe complications such as uterine injury, infection, or excessive bleeding are rare, but still possible. Therefore, it is crucial to strictly follow your doctor's instructions and see a doctor immediately if you experience any unusual symptoms.
What should be avoided after hysteroscopy?
After a hysteroscopy, there are precautions to take to prevent complications and allow the uterine cavity to recover completely. These include:
- Avoid sexual intercourse for approximately one week.
- Avoid strenuous exercise for 1-2 days.
- Do not use any inserted devices into the vagina, such as tampons or menstrual cups, until your body has fully recovered.
- Do not ignore any unusual symptoms, such as high fever, severe abdominal pain, or excessive bleeding. Seek immediate medical attention.
/Vibhavadi%20Hospital%20-%20Nov%2012%20(%E0%B8%9C%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%B2%E0%B8%95%E0%B8%B1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%AA%E0%B9%88%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%81%E0%B8%A5%E0%B9%89%E0%B8%AD%E0%B8%87%E0%B8%A1%E0%B8%94%E0%B8%A5%E0%B8%B9%E0%B8%81)%20(7).jpg)
How many days does it take to recover after hysteroscopy?
Most patients recover quickly and can return to their daily routines within 1-2 days, as it is a day surgery. However, in cases of complex abnormalities, such as the removal of large fibroids, a 2-3 day recovery period may be required, and it is recommended to avoid strenuous activities until fully recovered.
Hysteroscopy at Vibhavadi Hospital
Hysteroscopy at Vibhavadi Hospital offers a modern and personalized treatment experience. Our expert gynecologists and high-tech endoscopic equipment allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of abnormalities within the uterine cavity, including polyps, fibroids, and adhesions. The surgery uses small incisions, is less painful, and allows for faster recovery, with patients able to go home the same day. Close post-operative care is provided, ensuring patients confidence in our standards of service, convenience, and the best possible outcome for every woman's health.
Summary
Hysteroscopy is a safe and quickly recovering procedure suitable for women with irregular menstruation, infertility, or suspected uterine abnormalities. Advantages include a clear view of the uterine cavity, less pain, small incisions, and the ability to examine and treat abnormalities in a single procedure. After the procedure, rest, avoid strenuous exercise, and refrain from sexual intercourse for a while. Common symptoms include spotting, mild abdominal pain, or slight fatigue. Serious complications are rare, but if there is excessive bleeding, severe abdominal pain, or high fever, seek immediate medical attention. Following your doctor's instructions can help speed up recovery and minimize risks.
Interested in health screening to identify risks or abnormalities? Visit Vibhavadi Hospital, where we have expert doctors and state-of-the-art endoscopic equipment for accurate diagnosis and treatment tailored to each individual. Minimally invasive, with faster recovery, giving you peace of mind and good health.